- Abandoned agricultural fields
- Abandoned industrial lands
- Fields that are mowed infrequently
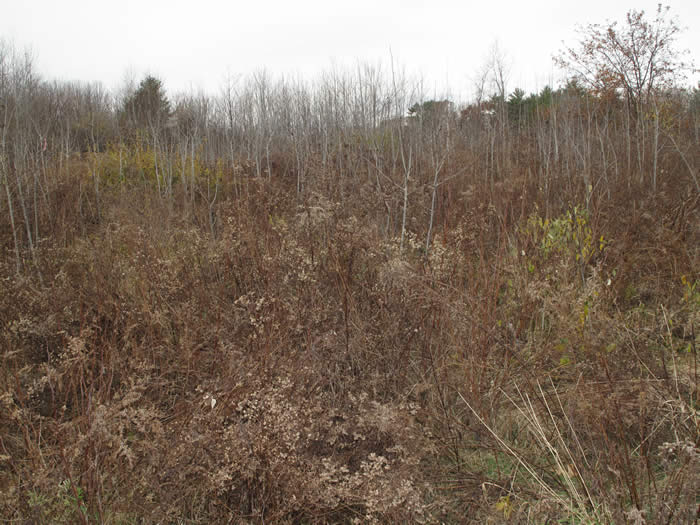



- Gray dogwood
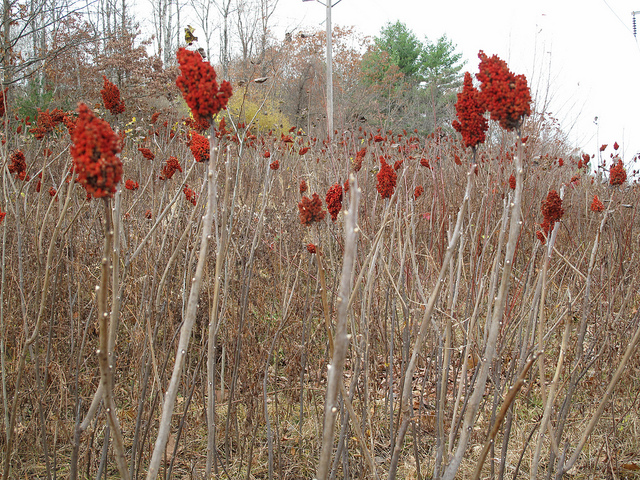
- Sumac
- Aspen
- Juniper
- Pine
- Raspberry
- Blackberry
- Meadowsweet
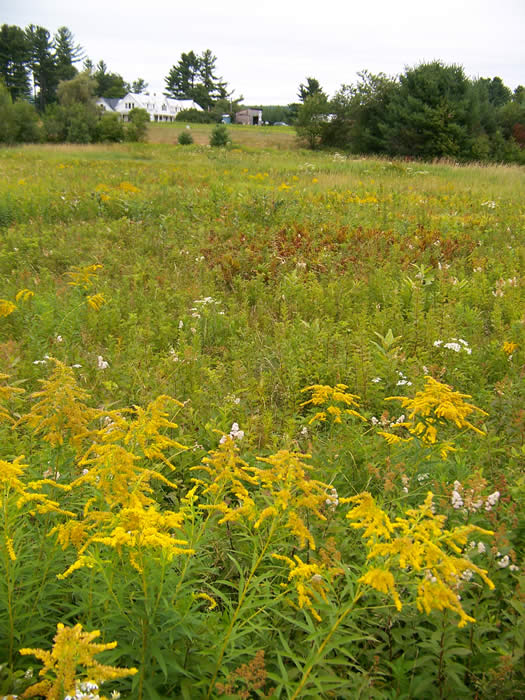
- Golden rod
- Milkweed
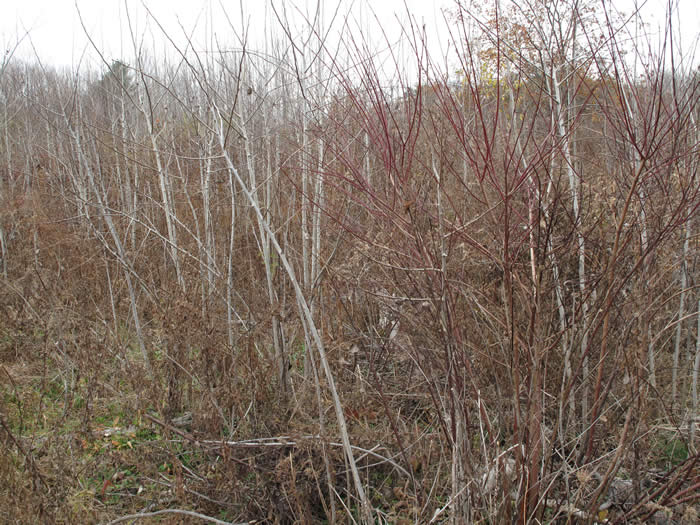


- American woodcock
- New England cottontail
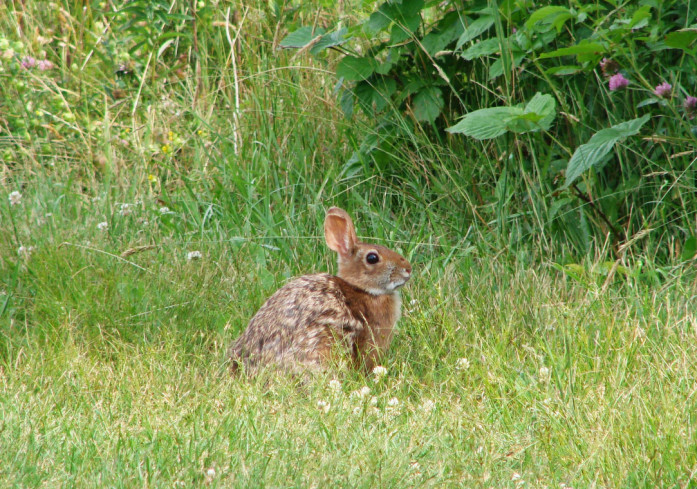


- Shrubs are no longer dense, and vertical structure is lost
- Tree species are beginning to get large and over-top shrub species
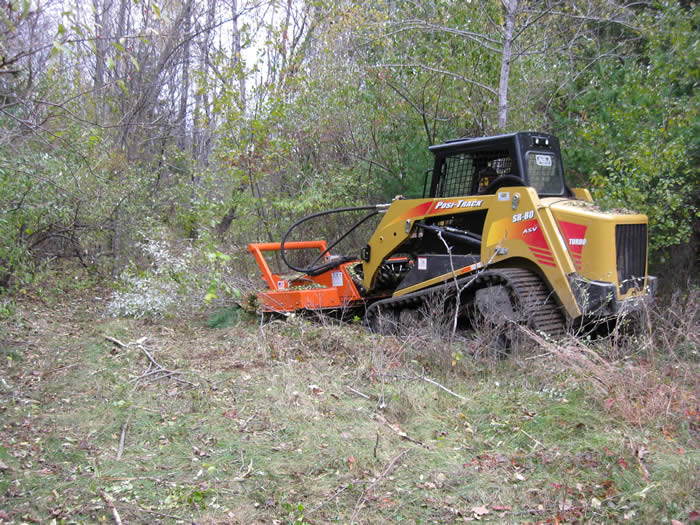
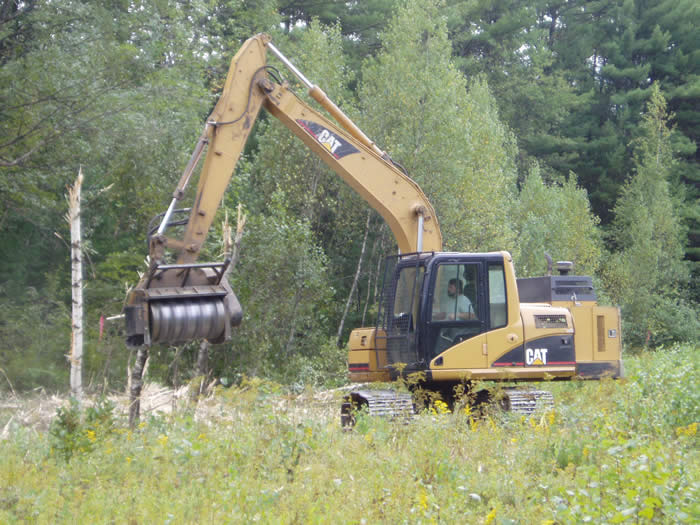
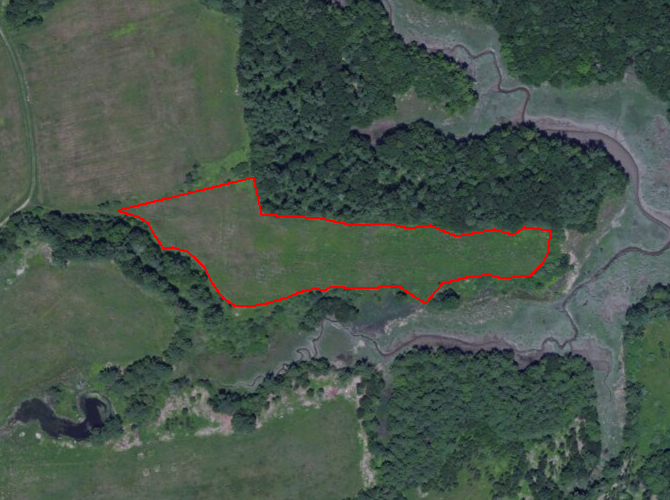
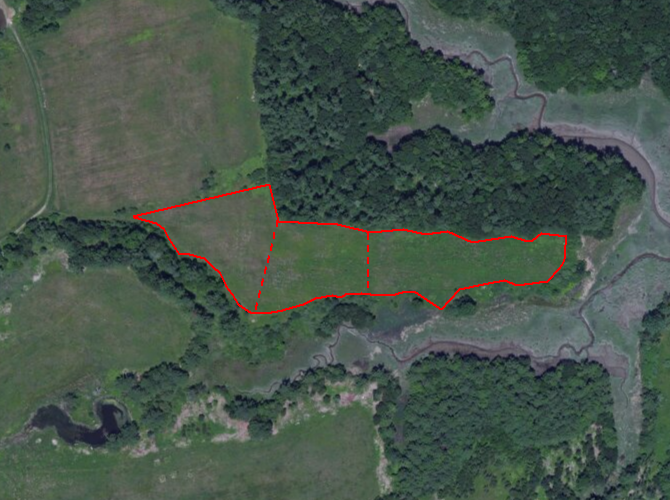


4. Manage on a rotation, never eliminating all the habitat at once. Continue cutting management blocks over time, approximately every 5-7 years with a brush hog or every 10-15 years with a bronotosaurus.
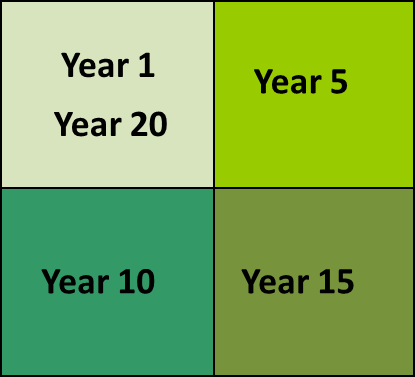
It is often possible to create old field shrublands habitat by simply allowing a field to revert to shrubs. This can be supplemented by planting native shrubs, but it is often unnecessary.