More than 50% of New Hampshire's population depends on groundwater supplies for drinking water. Groundwater particularly important during the dry periods when it is often the primary source of water for streams and rivers. Groundwater is found below the surface between particles of sands, silts and clays or in the cracks and fractures of bedrock. Aquifers are saturated zones in sediments, such as sand and gravel, and in fractured rock formations that receive, store and transmit water to wells and springs. Groundwater is recharged when rain and melting snow percolate down into the saturated zones. While groundwater quality in NH is generally good, groundwater is vulnerable to contaminatination from a variety of sources, e.g. chemical spills, leakage from landfills and underground storage tanks, septic systems, road salt, etc. Wellhead Protection Areas (WHPA) are the areas around a public water supply. The state's wellhead protection program enables municipal authorities, water suppliers and other local entities to delineate protection areas, identify potential contamination sources and actively manage land use in the WHPA. Increased impervious surfaces which reduce infiltration to groundwater and increase surface runoff can have a significant effect on recharge to groundwater supplies.
As the global, national, regional and local levels, ground water is the largest distributed store of fresh water and plays a central part in sustaining ecosystems and enabling human adaptation to climate variability and change. The strategic importance of ground water for water and food security will probably intensify under climate change as more frequent and intense climate extremes (droughts and floods) increase variability in precipitation, soil moisture and surface water. Protection of locally important aquifers by protecting the lands that overlie them is an important priority for maintaining adequate drinking water supplies into the future.
Basic NRI - What to Include:
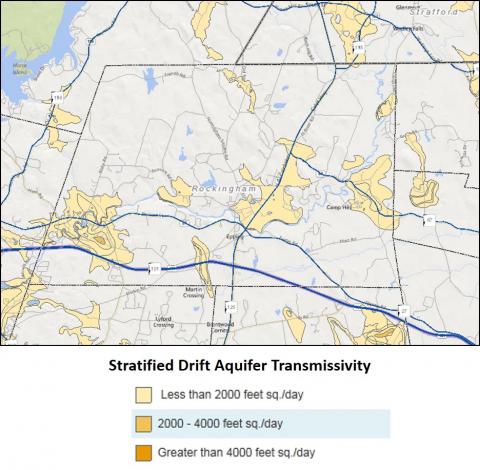
Many of New Hampshire's reliable aquifers are found in deep, coarse-grained stratified drift deposits (sands and gravels), which were deposited by glacial meltwater at the time of deglaciation. The location and extent of these aquifers should be mapped along with transmissivity values which are available through GRANIT and GRANITVIew. See Sample Water Resources Map in the Sample Map Set to view stratified drift aquifer information. Transmissivity is a measure of how much water can be transmitted horizontally in an aquifer. Higher transmissivity values indicate greater groundwater availability. Wellhead protection areas can also be shown on the map.
CLIMATE CHANGE As the world's largest distributed store of fresh water, ground water plays a central part in sustaining ecosystems and enabling human adaptation to climate variability and change. The strategic importance of ground water for global water and food security will probably intensify under climate change as more frequent and intense climate extremes (droughts and floods) increase variability in precipitation, soil moisture and surface water. The strategic importance of ground water for global water and food security will probably intensify under climate change as more frequent and intense climate extremes (droughts and floods) increase variability in precipitation, soil moisture and surface water.
Detailed Inventory Studies:
A Comprehensive Ground Water Resources Study can help a community interpret and understand their groundwater resources in more depth. By analyzing existing groundwater information (e.g. groundwater quality data, well locations and yields, etc.) and providing any additional necessary documentation, the comprehensive study can help to further identify areas where groundwater protection might be appropriate, look for potential conflicts between land use and groundwater protection, and address wellhead or groundwater protection plans. This type of assessment would require professional expertise.
Additional Resources:
NH DES Groundwater Bureau
NH DES Source Water Protection Grants Program
NH DES Source Water Protection
Protecting Groundwater Resources