Identification, Care and NH Big Trees
Yard & Street Trees
Common Questions
Our latest count shows 86 native tree species in New Hampshire. The exact number is hard to determine because some are rare, some are mostly found as shrubs, and others can be distinguished from each other only by the most determined dendrologist. This List of New Hampshire Native Trees lists species that are native to at least part of New Hampshire and capable of growing into a tree.
In Native Shrubs, Subshrubs & Lianas of New Hampshire we list 235 species of native shrubs, subshrubs, and lianas. The exact number is tricky to pin down because some shrubs also occur in tree form and others are subshrubs (dwarf shrubs or perennial plants that are woody only near the base, where new growth above the base dies back each year).
Helpful Characteristics for Identifying Shrubs (and a few trees) in Winter lists key identification points for over 40 shrubs (and some trees). It includes colored pictures of twigs and buds.
Distinguishing Characteristics of 56 Forest Trees is summary of characteristics common forest trees.
Know Your Trees from Cornell describes 50 trees.
Anyone interested in tree id needs to have at least a passing familiarity with dichotomous keys. This Wisconsin site for kids walks you through using a Dichotomous Key. Here is a pdf version as well.
Michigan State University has a versatile site with four keys moving you through to identification. Easy to use and fully illustrated.
"Go Botany" provides this useful site for New England plants.
Forest Biology and Dendrology at Virginia Tech includes tree identification fact sheets for 450 species. Figure out your unknown specimen, using the twig or leaf key. Easy to use and fully illustrated.
The National Plants Database is a single source of standardized information about plants. It covers vascular plants (such as trees), mosses, liverworts, hornworts, and lichens of the US and includes names, checklists, automated tools, identification information, species abstracts, distributional data, crop information, plant symbols, plant growth data, plant materials information, plant links, references, and other plant information.
A Partial Listing of Publications on Tree and Shrub Identification should help serious students find additional books to add to their library.
Here is a series of short videos for over 130 trees and counting! They are produced by the State University of NY, College of Environmental Science and Forestry

The NH Big Tree Program staff and volunteers compiled a map of some of the state's biggest trees in a convenient digital map. that can be viewed by the public. It contains information on tree size, tree locations and champion status.
The NH Big Tree Program is sponsored by UNH Extension, the NH Division of Forests and Lands and the Society for the Protection of NH Forests.
(Adapted from the Nebraska Forest Service with permission)
For the trees that survived the most recent ice storm, the job of repairing them and bringing them back to good health has only just begun. Before broken branches are removed, they should be examined carefully, and proper pruning methods should be used to minimize the damage from the pruning cuts. Trees too large to handle from the ground should be pruned only by professional arborists.
Branches to Remove
Safety is the first consideration in removing branches from storm-damaged trees. All branches that are loose should be removed as soon as possible to eliminate the chance of injury or damage if they were to fall. Other branches that are cracked or broken should be removed after the loose branches are gone. Branches that did not break under the weight of the snow but were bent over may have internal cracks or other hidden damage, especially if these branches have not returned to their original upright positions. These branches may become hazards in the future and should be considered for removal. A branch (or trunk) that was partially stripped of its bark when an attached branch pulled away should be removed if more than a third of the original circumference is lost. These branches will always be structurally weak and may become serious hazards if they are allowed to remain and get larger.
Making Pruning Cuts
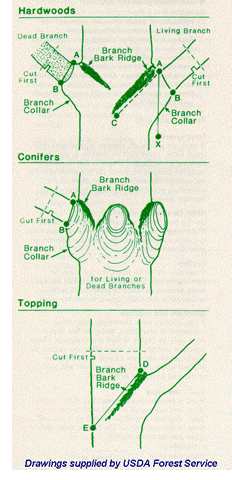
Pruning cuts should be made so that only branch wood is removed and the trunk or supporting stem is not injured. If only branch wood is removed, the wound is smaller, the tree will be able to seal the wound more effectively, and the chance of problems with wood decay will be greatly reduced.
To locate the proper place to make a pruning cut, look for the "branch bark ridge" on the upper surface of the union of the branch with the supporting stem. This is a line of bark that has been pushed up as the branch and supporting stem have grown. Some branch unions will not have this if they did not form properly. Instead they will have the branch simply pressing into the supporting stem, forming a sharp V-shaped union. At the base of the branch, and mostly on the underneath side, look also for the "branch collar," which is a slightly swollen area of stem tissue that wraps around the base of the branch. A proper pruning cut begins just outside the branch bark ridge and angles down and slightly away from the stem, avoiding injury to the branch collar. Do not make flush cuts that remove the branch collar. Wounds created by flush cuts cause substantially more injury to the tree than wounds left by proper pruning. Branches should be pruned using a series of three cuts as shown in the figure: two to remove the weight of the branch (first under then over the branch), then the final pruning cut.
Branches that have pulled away from the trunk should be removed at the bottom of the split. Avoid causing any additional damage to the trunk. Remove any loose bark, but do not cut into bark that is living and still attached.
When to Prune
The only pruning that should be done at this time is the removal of broken branches. Leave the fine pruning and finishing cuts until late winter or early spring. All pruning cuts will dry out to some degree during the winter. Dieback of the inner bark around a pruning cut can be minimized if the final pruning is left until just before the tree begins to grow in the spring.
Pruning "Don'ts"
Never top trees. Topping creates serious hazards and dramatically shortens the life of a tree. Never use paint or wound dressing to cover wounds. These materials do not help the tree and actually interfere with the tree's wound sealing process.





